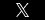If you have recently retained an attorney to represent you in your divorce proceeding, chances are that you already have or will soon receive what is known as a “litigation hold letter.” Although you will inevitably receive many other letters and forms at the onset of your divorce proceeding, it is important to pay close attention to this particular letter.
Family law attorneys will typically send their clients a litigation hold letter right after the attorney has been retained by the client. These written directives are also known as “preservation letters” or “stop destruction requests.” In anticipation of potential future litigation, a litigation hold letter or notice is essentially written instructions requiring that you preserve all documents and electronically-stored information (“ESI”) which could be relevant evidence. ESI refers to any information that is created, stored or utilized with computer technology. This includes emails, computer and network activity logs, digital recordings, voice mails, web-enabled cell phones and portable devices, internet files, computer drives, disks, CDs, etc.
Generally, the obligation to preserve evidence begins when a party knows, or reasonably should know, that the evidence is relevant to future or current litigation. In other words, the evidence is reasonably calculated to lead to the discovery of admissible evidence, is reasonably likely to be requested during discovery, or is the subject of a current discovery request from the opposing party. Thus, if not already triggered, receipt of the litigation hold letter will trigger the duty to preserve relevant evidence.The scope of the hold depends on the specific facts of the case and what is likely to be at issue in future litigation. Typically, the hold will apply to all sources of data including emails, calendar entries, cell phones, accounting software, hard drives, thumb drives, contacts and task lists. Most documents today are in digital form, which is why preservation of ESI is particularly important. This does not mean that you have to save every single email or scrap of paper, but you should suspend routine destruction of documents and ESI as it relates to relevant evidence that might be useful to your opposing party. Even if your hard drive or phone breaks, for example, you need to refrain from disposing of it until your attorney says it’s okay.
If you have any questions before you delete anything or throw something away, you should speak with your attorney because there are severe penalties for what the court deems to be the destruction of evidence. You may be exposed to possible liability and sanctions. For instance, the Court may prohibit you from presenting certain evidence yourself, the court may decide issues without any input from you or the court may even make you pay for the recreation of the lost or damaged electronically stored information.
Continue reading
 San Diego Divorce Attorneys Blog
San Diego Divorce Attorneys Blog